Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMH2NMY)
| Drug Name |
Mepivacaine
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Carbocaine; Mepivacaina; Mepivacainum; Mepivicaine; Scandicain; Scandicaine; Scandicane; Arestocaine HCL; Carboplyin Dental; Isocaine HCL; Carbocaine (TN); Carboplyin Dental (TN); D-mepivacaine; DL-Mepivacaine; Mepivacaina [INN-Spanish]; Mepivacaine (INN); Mepivacaine [INN:BAN]; Mepivacainum [INN-Latin]; Polocaine (TN); Polocaine-Mpf; S-Ropivacaine Mesylate; D(-)-Mepivacaine; N-Methyl-2-pipecolic acid, 2,6-dimethylanilide; N-Methyl-2-pipecolic acid, 2,6-xylidide; N-Methylhexahydro-2-picolinic acid, 2,6-dimethylanilide; N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-1-methyl-2-piperidinecarboxamide; N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-1-methylpiperidine-2-carboxamide; (+-)-1-Methyl-2',6'-pipecoloxylidide; 1-METHYL-2',6'-PIPECOLOXYLIDIDE
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anesthetics
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
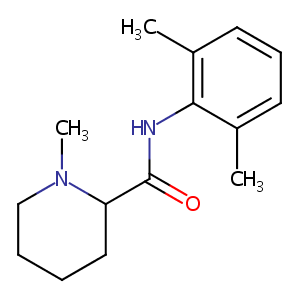 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 246.35 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 1.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Mepivacaine (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 3 | Critical Evaluation of Human Oral Bioavailability for Pharmaceutical Drugs by Using Various Cheminformatics Approaches | ||||
| 4 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 5 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 6 | Block of neuronal tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ currents by stereoisomers of piperidine local anesthetics. Anesth Analg. 2000 Dec;91(6):1499-505. | ||||
| 7 | Long QT 1 mutation KCNQ1A344V increases local anesthetic sensitivity of the slowly activating delayed rectifier potassium current. Anesthesiology. 2006 Sep;105(3):511-20. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200609000-00015. | ||||
| 8 | Keidar S, Grenadier E, Palant A "Sinoatrial arrest due to lidocaine injection in sick sinus syndrome during amiodarone administration." Am Heart J 104 (1982): 1384-5. [PMID: 7148661] | ||||
